Continuous Raster Data Examples
The Label Data is the data that will be printed out onto the labels. Take me to the top of the page.

Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
Here are some examples of satellite data uses.
. Raster data is. The following code adds rows for missing. Visit Readers and Writers to list data formats it supports and see Filters for filtering operations that you can.
Use a familiar geom geom_bar and geom_raster combined with a new statistical transformation stat_bin. This data model often refers to so-called regular grids in which each cell has the same constant size. For example you can add values of NUMBER data type but not values of RAW data type.
312 Raster Data File Formats. In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. The MOD44B data product layers include percent tree cover percent non-tree cover.
PDAL is a C library for translating and manipulating point cloud dataIt is very much like the GDAL library which handles raster and vector data. Titaniumcopper alloys with fully equiaxed grains and a fine microstructure are realized via an additive manufacturing process that exploits high cooling rates and multiple thermal cycles. What is Raster Data.
It is converted to 30m by 30m resolution using center value aggregation. Site selection analysis can be performed with vector or raster data. Includes examples and sample code for the.
Each pixel has an associated value. 32 Managing GIS Files in ArcGIS. PDAL - Point Data Abstraction Library.
Or they can be commissioned to provide continuous delivery of data for example from a specific area. While any type of geographic data can be stored in raster format raster datasets are especially suited to the representation of continuous rather than discrete data. The original raster data of 4m by 4m resolution from hyperspectral images.
These properties cause Oracle to treat values of one data type differently from values of another. A subset of variogram models available in Rs gstat. It represents the location size and shape of the object in the earth ie building ponds mountains administration boundaries etc.
0 means a dot is not printed. The ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension provides a rich set of spatial analysis and modeling tools for both raster cell-based and feature vector data. Validation at stage 3 has been achieved for the MODIS Vegetation Continuous Fields data product.
Continuous and Discrete Raster Data. Spatial Data is available in two primary formats 1. Lets start with a couple of examples with the diamonds data.
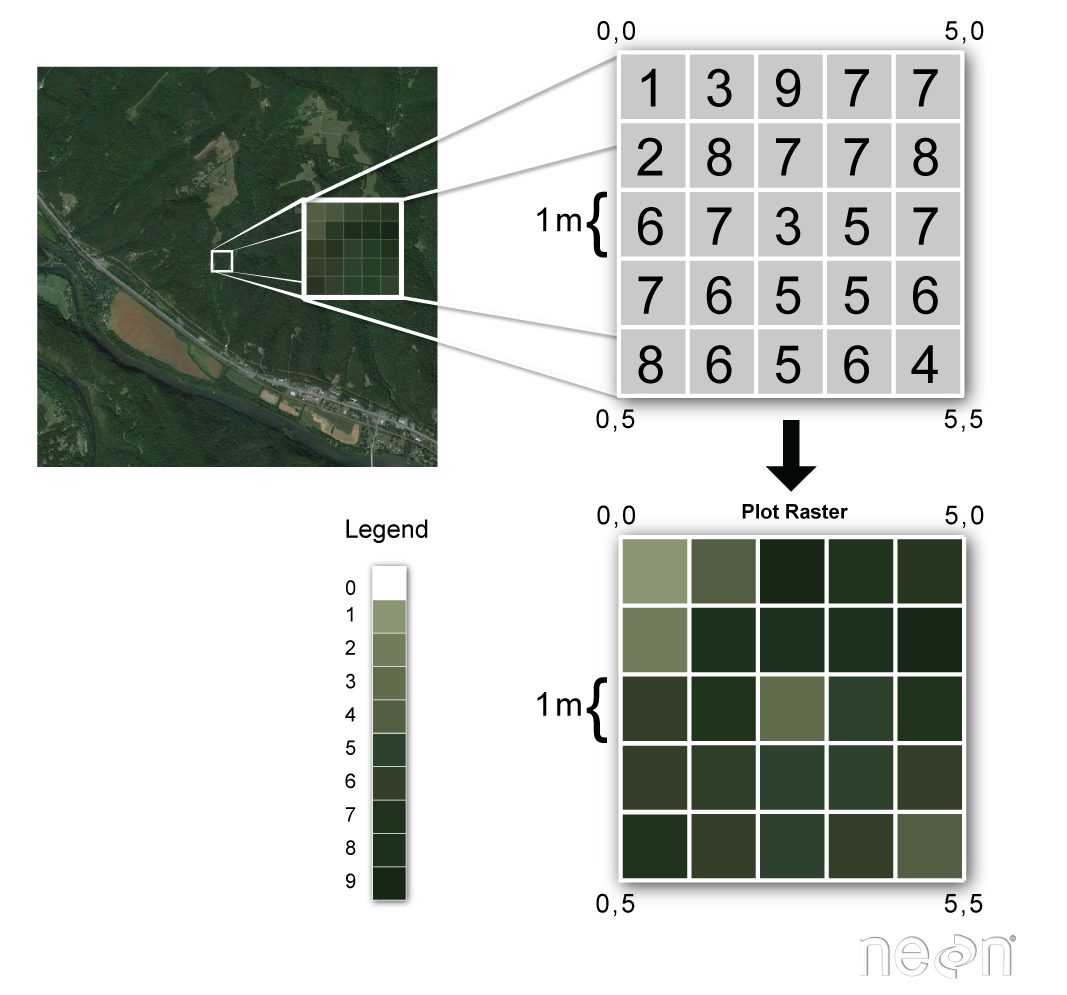
The scatterplot is a very important tool for assessing the relationship between two continuous variables. Examples of mathematical models are shown below. A grid of cells represents this data.
Raster data consists of pixels. In the previous plot there are many missing tiles. The capabilities of Spatial Analyst are broken down into categories or groups of related functionality.
For 3x3-chess with any beginning configuration small-board dots-and-boxes small-board-hex and certain endgames in chess dots-and-boxes and hex. Knowing the categories will help you identify which particular tool to use. The ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension provides a rich set of spatial analysis and modeling tools for both raster cell-based and feature vector data.
The spatial raster data model represents the world with the continuous grid of cells often also called pixels. These missing values are not unknown but represent values of class drv where n 0The complete function in the tidyr package adds new rows to a data frame for missing combinations of columns. Since the early 1960s with the availability of oracles for certain combinatorial games also called tablebases eg.
In computer graphics and digital photography a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of square pixels viewable via a computer display paper or other display mediumA raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixelRaster images are stored in image files with varying. These missing tiles represent unobserved combinations of class and drv values. The About page provides high level overview of the library and its philosophy.
Note that using gsn_csm_contour results in the raster bins at the edges being reduced to half width. Another class of techniques used with points that represent samples of a continuous field are interpolation methods. It is an array of binary data bytes.
Each cell has a value that represents information. 33 Managing a Map Project in ArcGIS. Available with Spatial Analyst license.
The figure is land cover map of before and after spatial aggregation. Spatial data is the physical representation of earth features. A new area for data mining has been openedThis is the extraction of human-usable strategies from these.
Learn more about how Apache Spark on Databricks supports the processing and analysis of large volumes of geospatial data. The next issue is vector to raster and raster to vector conversion which is often occurs in spatial analysis with two data types. Knowing the categories will help you identify which particular tool to use.
Each value manipulated by Oracle Database has a data type. Variables that may not be continuous probabilities00 may be best viewed via use of raster plots. Each cell has a value representing a property or attribute of interest.
Its size equals widthheight. The data type of a value associates a fixed set of properties with the value. ArcGIS MODIS-VIIRS Python Toolbox contains tools capable of decoding quality data layers while producing thematic quality raster files for each quality.
Raster data is cell-based and this data category also includes aerial and satellite imagery. The most significant bit of the first print data byte represents the lower pixel of the first line. Some examples of continuous data are.
The capabilities of Spatial Analyst are broken down into categories or groups of related functionality. These clearly show the bin and data resolution. However when the data is large.
1 means a dot is printed. Chemical concentrations and elevation surface are some examples of raster data. Raster data stores information of features in a matrix of cells or pixels organized into rows and columns either discrete or continuous.
An example of discrete raster data is population density. Oil depth across an open-water oil spill soil pH. The table at the end of this section lists all the available.
A raster data is a representation of images in a matrix of. Continuous data examples are temperature and elevation measurements. There are two types of raster data.

What Is Raster Data Help Documentation
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts

Discrete And Continuous Data Arcmap Documentation

Building Models For Gis Analysis Using Arcgis Analysis Remote Sensing Model
0 Response to "Continuous Raster Data Examples"
Post a Comment